Foundation Engineering
Construction of Foundation – Depth, Width, Layout and Excavation
Procedure for construction of foundation starts with decision on its depth, width and marking layout for excavation and centerline of foundation. Foundation is the part of structure below plinth level in direct contact of soil and transmits load of super structure to soil. Generally it is below the ground level. If some part of foundation is above ground level, it is also covered with earth filling. This portion of structure is not in contact of air, light etc., or to say that it is the hidden part of the structure.
Footing is a structure constructed in brickwork, masonry or concrete under the base of a wall or column for distributing the load over a large area.
Table of Contents
Depth of Foundation
Depth of foundation depends on following factors:
- Availability of adequate bearing capacity
- Depth of shrinkage and swelling in case of clayey soils, due to seasonal changes which may cause appreciable movements.
- Depth of frost penetration in case of fine sand and silt.
- Possibility of excavation nearby
- Depth of ground water table
- Practical minimum depth of foundation should not be less than 50 cm. to allow removal of top soil and variations in ground level.
Hence the best recommended depth of foundation is from 1.00 meter to 1.5 meter from original ground level.
Width of Foundation / Footings
The width of footings should be laid according to structural design. For light loaded buildings such as houses, flats, school buildings etc. having not more than two storeys, the width of foundation is given below:
- The width of footing should not be less than 75 cm for one brick thick wall.
- The width of footing should not be less than 1 meter for one and half brick wall.
Processes involved in Construction of Foundation
The processes executed in the foundation works are given below:
- Excavation of earth work in trenches for foundation.
- Laying out cement concrete.
- Laying the footing in case of raft or column construction.
- Laying Anti termite treatment.
- Laying Brick work up to plinth level.
- Laying Damp proof course on the walls.
- Refilling of earth around the walls
- Refilling of earth in the building portion up to the required height according to plinth level.

Fig.1: Excavation for Foundation of Wall

Fig.2: Concrete in foundation
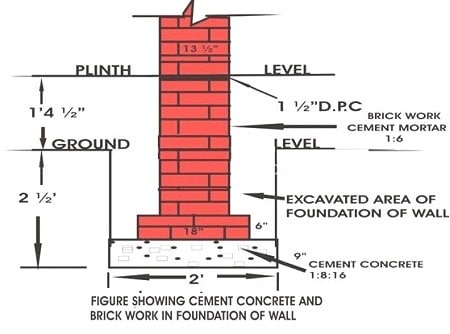
Fig.3: Concrete and Brickwork in Foundation of Wall
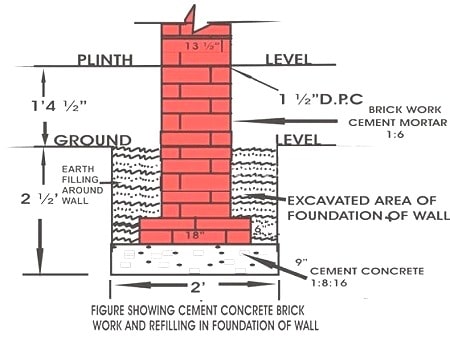
Fig.4: Concrete and Brickwork in Foundation Refilling
Precautions while designing a Foundation
- A foundation should be designed to transmit combined dead load, imposed load and wind load to the ground.
- Net loading intensity of pressure coming on the soil should not exceed the safe bearing capacity.
- Foundation should be designed in such a way that settlement to the ground is limited and uniform under whole of the building to avoid damage to the structure.
- Whole design of the foundation, super structure and characteristics of the ground should be studied to obtain economy in construction work.
Ratio of Cement Concrete and Mortar for Foundation
- The cement concrete 1:8:16 is generally used in the foundation of walls in construction work.
- In case of column raft cement concrete 1:4:8 is the best recommended ratio for it in the foundation.
- For brick masonry cement mortar 1:4 to 1:6 is used as loading condition.
In case of column and raft footings up to plinth level cement concrete 1:2:4 or 1:1.5:3 are used.
Soil having Safe Bearing Capacity
Dry coarse and well graded dense sand have maximum shear resistance and maximum bearing capacity. In general submerged soil and clay have less bearing capacity.
Precautions during Excavation for Foundation
The depth and width of foundation should be according to structural design.
- The depth of the foundation should not be less than 1 meter in case the design is not available.
- The length, width and depth of excavation should be checked with the help of center line and level marked on the marking pillars.
- The excavated material/ earth should be dumped at a distance of 1 meter from the edges.
- Work should be done on dry soil.
- Arrangement of water pump should be made for pumping out rain water.
- The bottom layer of the foundation should be compacted.
- There should be no soft places in foundation due to roots etc.
- Any soft/ defective spots should be dug out and be filled with concrete/ hard material

Fig.5: Excavation for foundation where root of tree exists

Fig.6: Excavation of wall in foundation root removed

Fig.7: Pit of root filled with hard material
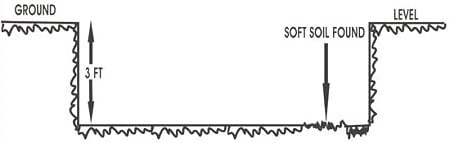
Fig.8: Excavation of foundation of wall with a patch of soft soil

Fig.9: Excavation of wall foundation with soft soil removed

Fig.10: Pit of soft soil filled with hard material
Demarcation / layout Procedure for foundation
The following procedure is recommended for demarcation of a building.
- For layout of a building baseline is marked on the ground either from center line of the road or from any permanent building nearby. This line helps to mark out the front of a building. Side baseline is also marked with the help of side structure or road or it can be marked with the help of first baseline or boundary of the plot.
- Fix temporary pegs at the center line of walls/columns on both sides of walls and columns in front and back side.
- Fix peg at the center line of walls/columns on both sides of wall and columns in left and right side of front of building.
- Check diagonals of the square or rectangle formed after fixing pegs.
- Construct marking pillars with pegs at a distance of 1.5 meter to 2 meters and their top surface should be plastered.
- Mark center line on the top of marking pillars with the help of thread (Soot) or with the Theodolite in big projects and the diagonal and other dimension should be checked.
- Level marking pillars on all corners of building and the top level is fixed at a proposed plinth level.
- Mark the foundation of walls/columns according to drawing on the ground with the help of centerline marked on the marking pillars .
- Mark foundation trenches on the ground with chalk powder.
- Excavate the foundation of the walls /columns up to required level and the excavation must be checked with the help of center line and level marking pillars to avoid any complication later on.
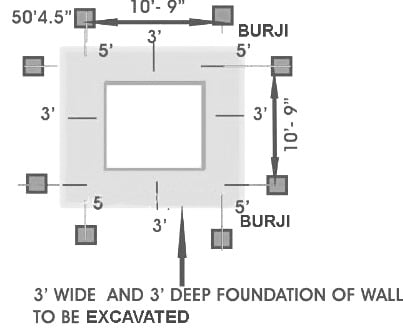
Fig.11: Excavation for foundation under wall
Advantages of Layout with the help of marking pillars
- It saves time for measuring and setting of point again and again at the time of construction.
- It increases the efficiency of mason and foreman for doing their jobs.
- Accuracy can be checked at any time at any step.
- If any mistake is found, it can be easily be rectified at early stage. It is very difficult to rectify the mistake in later.
- Cross check can be done by senior engineer in minimum time.
- A qualitative work is maintained.
Disadvantages for doing the work without layout
At some sites of work the contractor brings steel pieces, erects the same on the ground and start the work of excavation. In due course these steel pieces are just discarded. Thus no proper reference point is available while doing further jobs.
- It involves extra time for measuring the offset again and again.
- Accuracy can not be checked at early stage and it will be very difficult to rectify the same in later stage.
- It involves wastage of time and money while doing rectification. This also leads to bad quality of work.
Materials used during Setting up of Layout
- Leveling Instrument
- Long Nails
- Hammer
- Right Angle
- Steel Tape
- Thin Cotton Thread
- Bricks
- Cement
- Screen Sand
- Lime Powder
- Theodolite
Comments
Post a Comment